Naver ([nei·br] Hangul: 네이버/) is a Korean-language “Portal” which displays search results in several curated sections on a single screen, such as news, images, video, shopping, and advertising websites, and it is in fact South Korea’s Largest Search Engine.
Despite Google’s best efforts to expand its presence in Korea, Naver keeps dominating the market with around 58% market share. In this article, we will explore the characteristics of Naver SEO, its algorithm, what Naver properties are, and practical strategies to optimize your website for improved visibility and success.
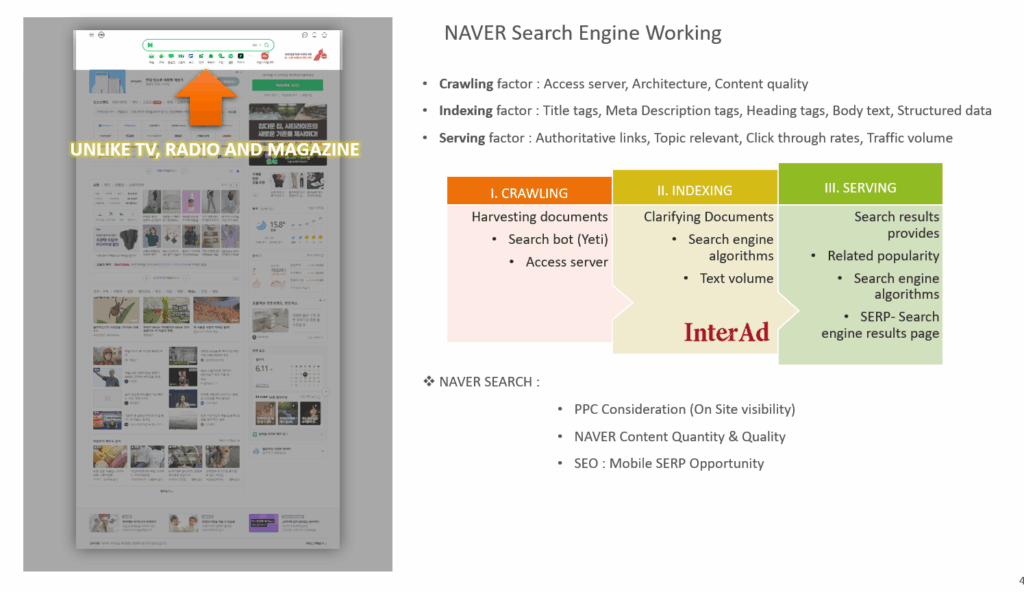
How Naver’s Search Works: Crawling, Indexing, and Serving
To better understand how SEO works within Naver, it’s helpful to break down the search engine’s technical workflow into three key factors: crawling, indexing, and serving.
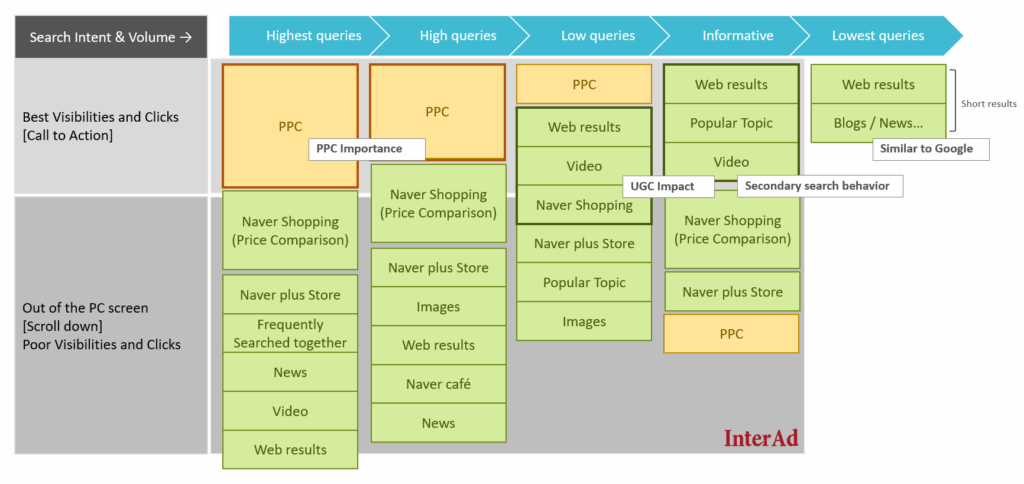
Naver SERP by Query Type and Intent
Naver has long prioritized Powerlink ads (PPC) at the top of its search results for high-volume E-commerce keywords.
However, there is a rise of long-tail queries, thus, the SERP has adapted and become more dynamic – shifting its layout based on search intent and content type.
For competitive and commercial keywords, PPC ads dominate the top of the page. But for queries involving authoritative or professional information, Naver may elevate trusted editorial or institutional content above ads.
This behavior mirrors Google’s YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) quality standards, where E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) plays a key role. Similarly, Naver increasingly favors reliable, user-satisfying sites by rewarding them with premium placement, even above paid results in some cases. The image below illustrates how Naver’s SERP works.
Naver Properties: Exploring the Ecosystem
Naver offers various properties that complement its search engine, allowing users to engage on multiple platforms. These properties include Naver Blog, Naver News, Naver Shopping, Naver Encyclopedia, Knowledge iN, Naver Maps, and Naver Café. Understanding these properties and leveraging them strategically will boost your website’s trust flow score, which will boos your website’s visibility and authority.
Powerlink Ads:
The keyword search advertising from Naver. This section of the SERP contains up to 10 advertisements for competitive keywords. You can check more in-depth about this topic in our article about Naver Ads.
Blogs:
When setting up a Naver Search Advisor (Webmaster Tools) account, Naver blog information is automatically provided, which can be used in the same way as any externally hosted blog on a platform like WordPress. While Naver claims that it does not discriminate against externally hosted blogs, it is worth noting that the search engine is better at crawling and indexing Naver blogs.
Posts:
As of the 30th of April 2025, Naver Posts is unavailable.
A stripped-down version of Naver Blogs. Rather than allowing you to the network by adding “neighbors” and engaging with them (like on Naver Blogs), it has a “follow” feature and focuses on the writer’s expertise on a particular topic.
Café:
This is a community-based platform, like Reddit or Baidu Tieba, that functions like a message board or forum for members with common interests to share knowledge and engage in discussion of that topic. Each “café” acts like a Subreddit with a niche focus and opportunity to build a community for information sharing. With over 100 different categories, it is the perfect place to find the perfect customer persona.
Learn how to advertise on Naver Café today.
Websites:
The website search result shows relevant web pages to the keyword; it looks pretty much the same as a Google search results page. However, on Naver the average number of organic results is four, so securing a spot on the first page can get quite tricky.
Encyclopedia:
This is similar to Wikipedia (and considered just as authoritative by Naver’s ranking algorithms) but much less restrictive, as it allows users to set up branded pages. On the search engine page, it is displayed as a vertical search result and features results drawn from Wikipedia as well as its platform.
Sounds interesting? Check out our article for more information on setting up a branded Wikipedia.
Knowledge iN:
This product takes data from a number of sources, including itself, and can appear prominently in search results, especially for searches phrased as questions. It functions similarly to Yahoo Q&A and Quora to provide users with answers to interrogative searches. Any user can post a question that other users can help to answer, across a multitude of different topics, and answers can be upvoted (in a similar fashion to a Reddit post) by other Naver users.
Naver Ranking System: How Features Are Indexed
Naver’s search index is made up of various elements, including basic matching information from web documents (such as page titles and body text), metadata needed for displaying search results, and feature-based indicators like quality scores, engagement metrics, and citation data. These features are developed and refined by Naver’s Web Search team to improve the relevance and accuracy of search rankings.
To manage this process, Naver uses a large-scale system known as the Web Search Refinement Data Pipeline. This system gathers documents from the crawler, processes the extracted features, and organizes them into structured data that can be integrated into the search index.
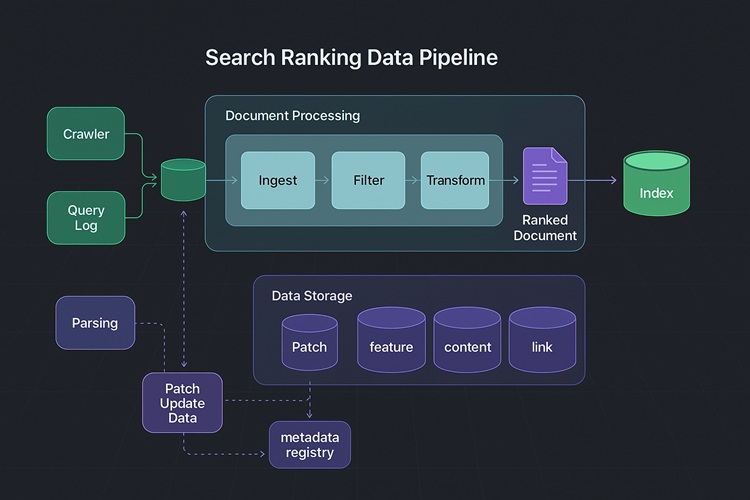
Web Search Refinement Data Pipeline/ Source: Naver Search & Tech
Metapub: Managing Feature Metadata
Given the variety and scale of features involved, Naver has developed a metadata registry system called Metapub. This registry keeps track of each feature’s structure, data type, storage location, and update frequency. When a new feature is created, the registry automatically detects it and notifies a feature updater module via API.
The updater fetches and transforms the data based on the signal and metadata, updates the database required for generating indexable documents, and triggers the delivery of new documents to the indexing system. This automated process ensures consistency and allows new features to be quickly integrated into the ranking system with minimal manual effort.
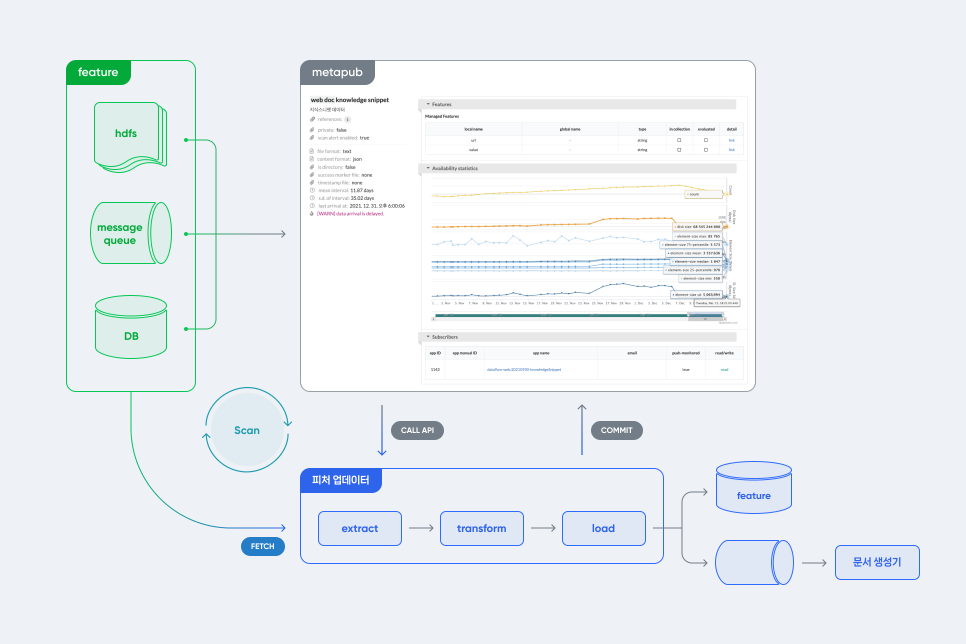
Feature Integration Using Metadata Registry/ Source: Naver Search & Tech
Priority Queue: Processing Features by Importance
Because the Web Search index processes massive volumes of data daily, not all updates can be handled equally. Some changes, like a document title update, are more significant than minor shifts in scoring metrics. To handle this efficiently, Naver uses a distributed priority queue system to assign and manage feature importance.
Features are placed into the queue according to their priority. When a new document needs to be generated, the system fetches the most important updates first. Duplicate updates are filtered out using timestamp comparisons, and the final structured document reflects only the most relevant and current information.
Through this system, Naver can minimize delays in indexing high-impact updates while conserving resources and maintaining the quality of its search results.

Naver’s algorithm explained
Naver’s algorithm has undergone significant changes over the years to enhance user experience and combat spam. Initially relying on keyword density, the algorithm now incorporates factors like relevance, user behavior, social signals, and page quality. Fresh and original content is favored, while the comprehensive rank (C-Rank) system evaluates the popularity and influence of websites.
P-Rank:
This algorithm uses similar global web standards to those employed by Google, looking at certain search engine optimization (SEO) criteria of a website to determine its quality, and was introduced by Naver in an attempt to make its organic results higher quality. Using a form of artificial intelligence data processing, this algorithm processes a number of ranking factors to ascertain the quality of a webpage and its relevance to a query. These include website crawlability and accessibility, page optimization and metadata, website structure and internal linking, mobile usability, number and quality of backlinks pointing to a website, and social media signals. Due to Naver’s dependence on paid advertisements, there are definite limitations on the effectiveness of SEO on the search engine, but paying attention to these metrics will help sites rank highly.
C-Rank:
This is the algorithm that applies to the Blog section in Naver. It uses content, context, and chain metrics to rank search results and identify the authority, popularity, and reliability of user-generated content. The “chain” metric refers to conversion, a marketing term that means how many people have visited your content/page as a measure of popularity. The algorithm determines the authority of each content creator, categorizing webpages by thirty-one different types depending on the title tag and the content. Naver uses deep learning technology to determine different content types, but many blogs are not favored by this algorithm as it prioritizes those with high rates of traffic and gives the top spots in its rankings to those deemed to have the most authority on a specific subject.
Deep Intent Analysis (DIA):
The DIA algorithm looks to identify the user’s search intent based on the content they access and reflects this in the search engine rankings. It uses various metrics to measure a user’s intent or preference for specific content, including time spent on a web page, the number of shares of a blog, comments, etc. It is unlikely that Naver will disclose the entirety of the algorithm, but the best tactic to keep content ranking high in search results is increasingly creating content that satisfies the user. The DIA algorithm, paired with the P-Rank algorithm in particular, means that Naver’s search results are showing more similarity to Google’s than ever before. Previously, the number one way to rank high in Naver search results was considered to be up-to-date content, mainly created on Naver Blog. Now, however, the search engine includes more external content and web pages, and it is necessary to satisfy all three algorithms in order to stay high in Naver’s rankings.
How to Optimize for Naver SEO: Effective Strategies
Here we have listed some things marketers should have into account when trying to get better organic visibility in Naver Search Engine.
On-Page SEO:
- Open a Search Advisor Account and set it up to have better insights into your website’s performance on Naver. Comply with Search Advisor technical recommendations – read this Search Advisor article to learn how to use Naver’s Search Advisor.
- Do a thorough keyword research. Keyword research is always an important step when doing SEO, but the tools that marketers use when researching for Google usually don’t have access to Naver’s database. To check accurately keyword volume on Naver, you will have to open a Naver Ads Account and explore their Keyword Tool. Check out InterAd’s ultimate guide to the data lab tool for a more comprehensive yet simple deep dive.
- Concise Titles and Descriptions: Craft relevant and concise titles and descriptions that align with your brand. Limit your titles to 40 characters or less and avoid keyword stuffing.
- User-Centric Content: This is no different from Google. Focus on providing informative and helpful content that satisfies users’ needs and preferences.
Off-Page SEO:
- Brand Building: It is no secret that Naver favors its own properties over organic results. Engaging with Naver properties like Naver Blog, Naver Posts, and Naver Knowledge will help you to build brand awareness and reputation.
- Content Marketing: Utilize platforms like Naver TV Videos, Naver Library, and guest posting to share valuable content and acquire quality backlinks.
- Listing Management: Register and optimize your business information on relevant platforms to improve visibility and credibility.
- Ratings and Reviews: Collect, monitor, and respond to ratings and reviews to enhance user trust and reputation.
How Naver’s SEO System Works
Like Google, Naver Search provides information on indexed and non-indexed pages.
Naver search results can be broadly categorized into three types: indexed pages, inaccessible pages, and pages excluded from indexing by meta robots.
The Naver indexing issue can be summarized as follows.
To increase competitiveness in Naver rankings, the following points should be noted.
- It is common for not all URLs to be indexed.
- Naver restricts the indexing of keywords related to adult content, harmful materials, gambling, speculative content, illegal financial services, or other prohibited topics. This is managed through its internal review system and the Search Term Verification Committee operated by the Korea Internet Self-Regulatory Organization (KISO).
- Naver Search has highly sophisticated language technology and reading systems. Noindex is required for content that is not suitable for indexing.
- URLs that do not need to be exposed in search results can be ignored, but separate measures are required for those that need to be indexed.
This can be seen in the priority control using the distributed priority queue introduced below.
Messages received with priorities defined by Naver’s key values are ranked by comprehensively considering timestamp information such as the collection document update time and feature update time.
To be included in the priority-assigned Key value, high-quality Korean content is required, as it is determined by the quality of Korean content in Naver’s index storage (Metapub).
Therefore, content-centric improvements by experts with experience in Korean blogs, content localization, news PR, etc. are essential.
Optimizing your website for Naver SEO presents a unique opportunity to tap into South Korea’s thriving digital landscape. By understanding Naver’s algorithm, leveraging its diverse properties, and implementing effective on-page and off-page SEO strategies, you can enhance your website’s visibility, authority, and user engagement. Stay updated on Naver’s advancements and refine your strategies to ensure long-term success in the South Korean market or get in touch with us for a free consulting session.
Source: Naver Search & Tech blog





